Health Checks

Mission control provides the ability to define and run periodic health checks against services, infrastructure, and applications.
1SyntheticSynthetic checks are periodically run by canary checker to directly test services/applications by generating requests using http, sql, mongo, redis, ldap, etc.
Passive checks consolidate alerts from monitoring systems like Prometheus, Datadog, Dynatrace, CloudWatch and ElasticSearch
Active infrastructure checks provision infrastructure (e.g. EC2 Instances, Kubernetes Pods) and then run synthetic checks against them to verify the ability to provision infrastructure. This allows detecting issues in infrastructure provisioning processes.
Integration checks run automated test suites using tools like Playwright, JUnit, Newman and K6 to validate end-to-end functionality across services and infrastructure.
Under the hood health checks are implemented using the open-source flanksource/canary-checker project
Metrics Exporter
In addition to returning a pass/fail status, health checks can export metrics to Prometheus, replacing the need for many custom prometheus exporters.
Scripting
Evaluate the health of checks using scripts in CEL, Javascript or Go Templating. Scripts can also be used to filter and transform alerts from external systems.
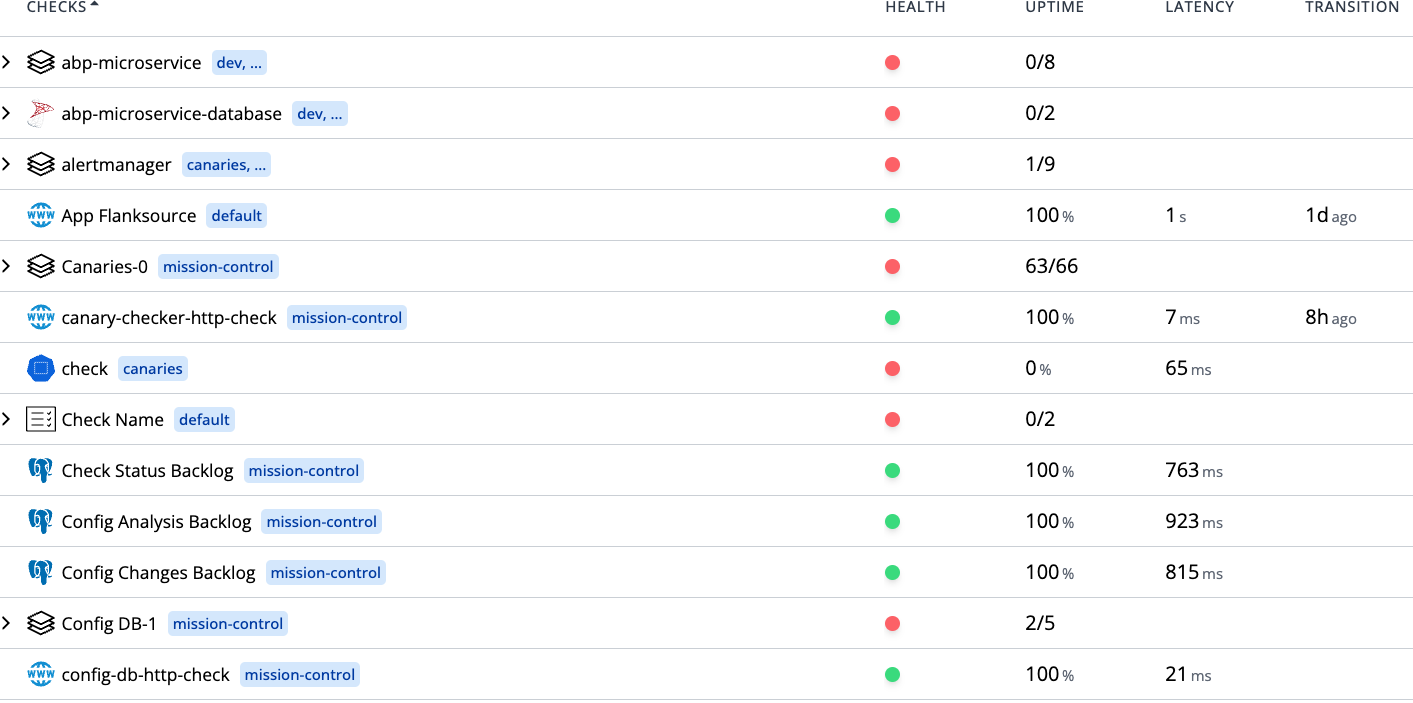
Dashboard
1DashboardThe health checks page provides a high level view of the overall health of all services, infrastructure, and applications. It surfaces recent failures and provides a high level latency and reliability metrics.
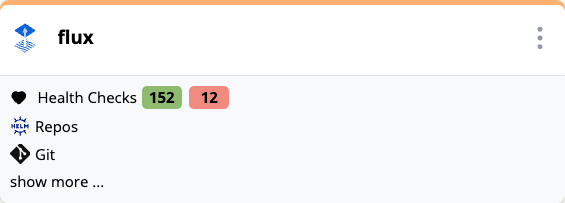
Health checks can be associated with components in a topology and then shows up in the topology card:
Prometheus metrics are exposed from health checks to provide high level visibility into latency, error rates and other metrics. This allows monitoring the health of services and applications using existing Prometheus alerts and Grafana dashboards.
Synthetic checks are periodically run by canary checker to directly test services/applications by generating requests using http, sql, mongo, redis, ldap, etc.